Startseite » services » Digitalization
Digitalization
Conception and implementation of digitalization offerings by introducing latest technologies and corresponding business models in order to open up new markets for the company.
- Business development by identifying the value proposition of digital products and services from the end customer’s point of view
- Create holistic implementation plans by identifying all business areas and partners involved, from development to sales
- Fast hands-on implementation through continuous and agile adjustments according to customer and employee feedback and in line with the company’s culture

„New technologies such as Cloud Services will change industry sustainably. In order to exploit the full potential of the digitalization offer, these innovations must be considered and implemented holistically and industry-specific, along the entire value chain of a company.“
Wilhelm Wiese

SAMPLE
A few thoughts on Disruption
… In the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution there are a lot of buzz words in every presentation. You can go to any conference or read just about any technical article and you will find at least some of them. What’s often missing, however, is reflection regarding what these terms mean in the context of industry. What will we gain? What will we lose? Why and in what ways are we being disrupted? And when we look a bit more closely at what’s going on, we must admit that technology itself isn’t disrupting anything. It’s the applications of technology that are shaking things up.
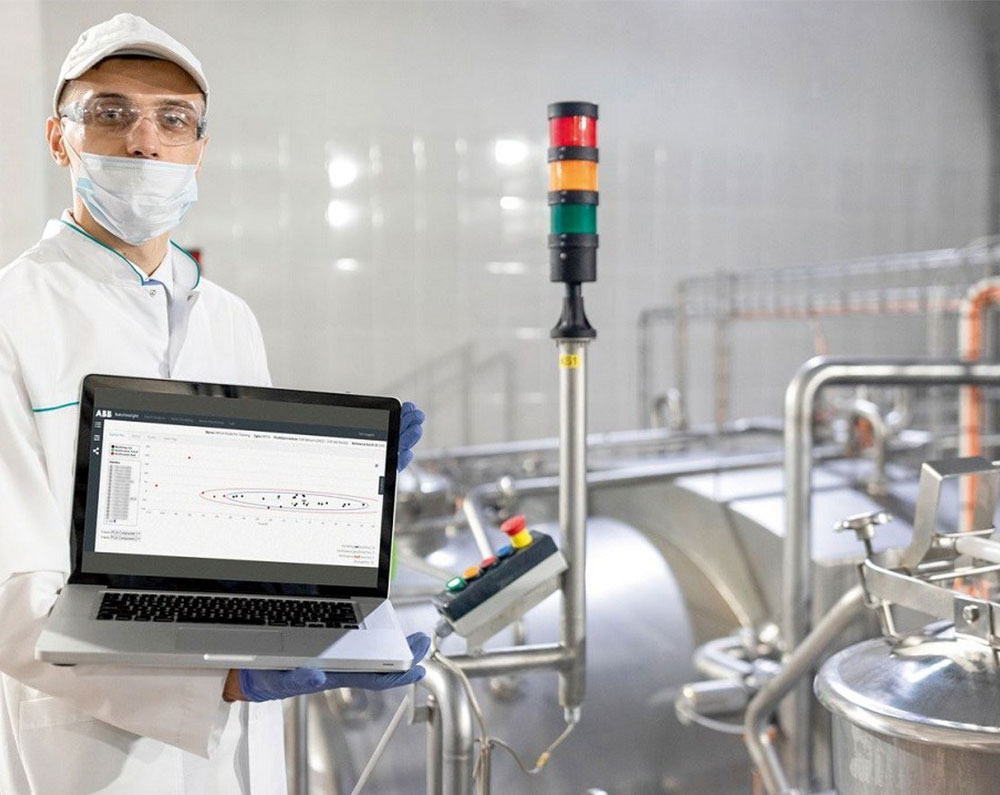
Take the Cloud, for instance. This is a general term that’s often applied indiscriminately to all sorts of developments in the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. But in point of fact, the Cloud is simply the core infrastructure that is used to deliver hosted software services over the Internet. A cloud is typically hosted in large, centralized data centers around the globe and its services are usually sold “on-demand,” typically by time of usage or storage volumes. The major benefit of the Cloud compared to a traditional local server-based infrastructure is that it is elastic, which means that associated computing and storage resources shrink and expand to meet the user’s changing needs.
However, in the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, access to the Cloud via the Internet and its often globally distributed infrastructure has engendered concerns regarding data residency, privacy and security. These concerns are particularly intense in those industries where intellectual property plays a key role. For example, it is easy to see why a pharmaceutical company that has spent tens of millions of dollars on research to develop a new medication will resist the temptation to upload any of its process-specific data to the cloud that might allow reverse engineering of its recipe. …
References
- Setting up the ABB Ability team at the ABB Corporate Technology Center (CTC), with a focus on cyber security for ABB's technology platforms, which has become the global COE (Center of Excellence) for all ABB products.
- Realigning the ABB Service Center for Automation Technology in Singapore for customer-centric consulting and operation and introducing value-based selling at the ABB locations in the Asia-Pacific region
- Pioneer of the third industrial revolution with a variety of projects like introducing Fieldbus technology from designing the architecture of automation systems to guiding the value creation of today’s asset management applications